Big Idea 5.5 and 5.6 Notes - Legal/Ethical Concerns and Safe Computing
Noting important parts of each lesson and answering the hack questions
5.5 - Lesson Notes
We talked a lot about copyright and how it is sometimes exploited to claim ownership of things that companies do not own purely because there’s some slight resemblance. Ultimately, we came to the conclusion that copyright as a concept is very important, but its execution leaves room for smaller creators or work inspired by a separate source to be exploited and blocked.
We also talked about how we would always expect credit for our artistic or academic endeavors; we wouldn’t want people stealing our essays, artwork or music compositions without clear credit.
On GitHub, we use licenses to ensure that our work is properly credited by giving instructions for the use of our code/content.
Hacks Reflection
When you create a GitHub repository it requests a license type. Review the license types in relationship to this Tech Talk and make some notes in your personal blog.
The licenses ask different things of those who wish to make work plagiar-inspired by ours. Some licenses, like the MIT license, allows for closed source versions of the original work as long as the original authors are credited. GPL, on the other hand, asks that no closed source versions be created; the work can be used in pretty much any other way aside from that.
In your blog, summarize the discussions and personal analysis on Software Licenses/Options, Digital Rights, and other Legal and Ethical thoughts from this College Board topic.
See the “Lesson Notes” section above.
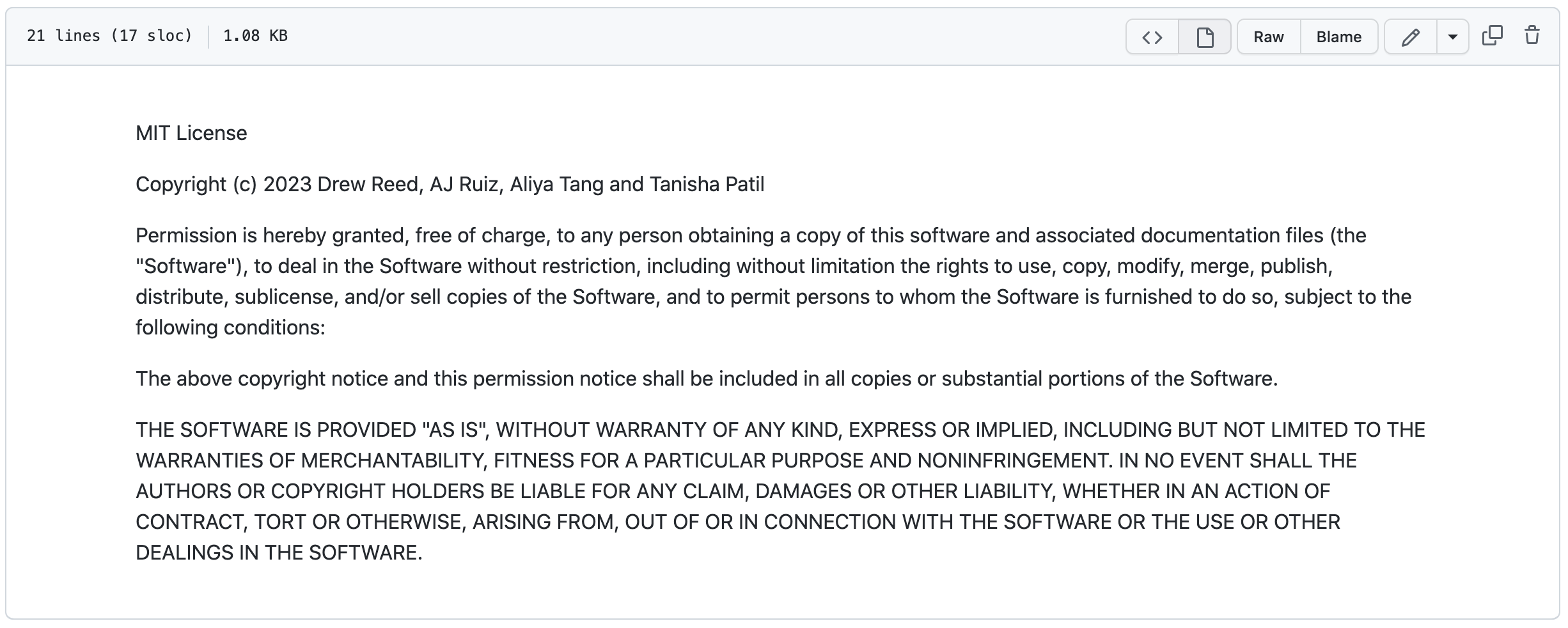
Make a license for your personal (blog) and Team repositories for the CPT project. Be sure to have a license for both Team GitHub repositories (frontend/backend). Document license(s) you picked and why. FYI, frontend, since it is built on GitHub pages may come with a license and restrictions. Document in blog how team made license choice and process of update.
Our group decided on an open source MIT license. Our site doesn’t provide one completely unique service. Instead, we apply our own takes on various existing ideas and collect them into a single service. With that in mind, it didn’t make sense to close off our work in a serious way; we just want credit for our original work.
5.6 - Lesson Notes
We started by talking a lot about what happens when we Google ourselves. Most of us said that we see people who have the same name, but others said they could find their picture and various other information about them on social media accounts, Linkedin, etc.
We talked about things we would be okay with being online (everyone was okay with names, but some didn’t want even photos, email, or any sort of means of contact available) and other things that we definitely wouldn’t want online (social security number, bank account information, computer and account passwords, daily schedule, etc.).
We moved on to talking about how we’re able to protect that information. Someone brought up two-factor authentication, and that moved us onto the topic of how we can protect this information. We talked about encryption and other types of personal identification for logins and symmetrical/asymmetrical cryptography, but never got to things like biometrics. We talked about two-factor authentication (like getting confirmation emails), and how we can avoid malware and phishing.
The latter brought us to a broader topic of how we can prevent the more vulnerable among us from being exploited by scammers and phising attempts. We talked about having the responsiblility to teach those who aren’t very tech-savvy (especially the elderly) about how those scams work and make sure they have resources they can go to in order to check if they are being scammed or not. I brought up that I think it’s important for search engines and other programs like remote-access software providers to take some responsibility in the problem when their programs are used for these scams; this would mean Google, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, etc. would have to pay more attention to fake popups on misspelled URLs, and remote access software should have clearer disclaimers about possible scams or even have certain limits on remote access from across the globe (since most people who run tech scams in the United States don’t live locally, but instead in India).
Hacks Reflection
Describe PII you have seen on project in CompSci Principles.
There were a bunch of projects that were presented last week that advertised some kind of personal login system and leaderboard system. However, on a more personal level, the grade checker software, for example, asked for some more personal information about your school (which would locate you), as well as your name, grade (close to age), and grades. This would require some kind of strong encryption.
What are your feelings about PII and your personal exposure?
Personally, I am fine with my name, picture, and age being out there. I do theatre, so it’s kind of a good thing to have my name out there. When you look up my name and look past all of the other old white guys, you’ll find local newspaper articles that talk about my roles in Del Norte productions, which makes me a little worried about being found by people like my overseas online friends or people across the globe who watch my YouTube channel (it’s not huge and is mostly inactive, but when I upload something in the near future, I’ll gain some more viewership). Overall, I’m very cautious with my personal information. I get squeamish when a trustworthy site asks me to input personal information; even sites like my bank concern me. I know a lot about scams, though, from watching videos of people leading scammers on or stealing their information, so I feel that I’ll be able to avoid having my personal information stolen by some kind of scam.
Describe good and bad passwords? What is another step that is used to assist in authentication.
Good passwords are passwords that contain a unique set of characters that cannot be guessed by knowing other personal information about you. Bad passwords are predictable knowing you or cliche, like “password1234” or your name backward. Two-factor authentication, such as when you’re sent a confirmation email, is a good way to confirm that you’re really the person accessing your account, since only the person with the email’s password can use the email to confirm their identity.
Try to describe Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption.
Symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data, while asymmetric encryption uses two keys: a public encryption key and a private decryption key.
Provide an example of encryption we used in AWS deployment.
AES-256 encryption is one of the defaults for AWS.
Describe a phishing scheme you have learned about the hard way. Describe some other phishing techniques.
I don’t know what it was that I downloaded (I download a lot of dubious game roms for emulators, so there’s a lot it could’ve been), but something gave me a virus that just opened up Tor browser to (what I’m assuming is a) fake shopping page. I’m pretty sure trying to buy any of the items would have asked me for personal information that it would just steal.
I watch lots of videos about various tech support scams from people like Kitboga and Jim Browning. There are scams that involve fake refunds that claim to refund way more money than intended (by editing the HTML of your bank page), and you have to pay it back with gift cards. Other scams ask for you to advertise fake house listings for them, then redirect interested buyers of the fake ads to the scammers.